There are numerous benefits of OLED panels. They are thinner and brighter than typical LCD screens and offer superior color accuracy and contrast (adding better blacks). It’s no wonder that smartphone makers are switching to OLED displays.
Even mid-range phones (such as the Xiaomi Mi 9 SE / Samsung Galaxy J6 Plus) have begun to include these highly-priced display panels.
However, there is one drawback to OLED displays, and that has to do with how the screen manages the brightness of low levels.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a technique used by most OLED panels to dim their brightness. This differs from DC dimming, which has been used to adjust the brightness levels of LCD panels.
Most people won’t be able to distinguish between PWM dimming & DC dimming, although a tiny percentage of the population will be influenced by the earlier technique. Since OLEDs make their way into mid-range and even budget smartphones, their user base is rapidly expanding.
Because of the enormous surge in AMOLED usage in recent years, you’ll commonly encounter comments on the internet like this.
To understand DC dimming, we must first know PWM dimming and how it may cause discomfort to some users.
What is PWD Dimming & How does PWM Dimming work?
PWM is an acronym for Pulse Width Modulation. The width of the light pulse is varied to adjust the brightness of the display panel, as the name indicates, in this technique.
Simply said, you can control how long the screen stays on or off. Decreasing the brightness causes the screen to stay off longer than it does on, giving the notion of lower brightness.
Following reading that, you’re probably thinking to yourself, “Wait a minute, the screen turns off once the brightness is low?” That’s something I’ve never noticed before!
Because pulses have a very high frequency (typically above 200Hz), the human eye will not be able to detect individual pulses. The human eye, on the other hand, averages out the quantity of light emitted through these pulses. The perceived brightness is determined by the ratio of the panel’s on and off states.
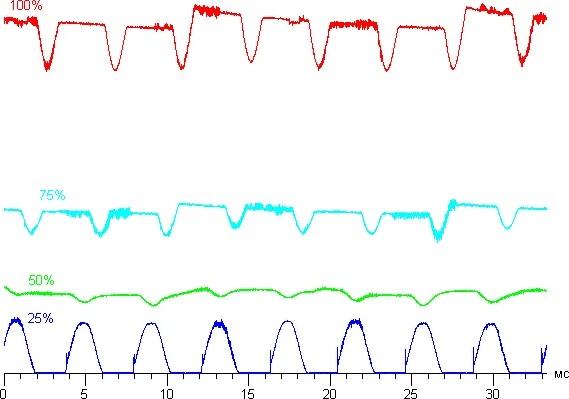
The figure below explains how PWM dimming works.
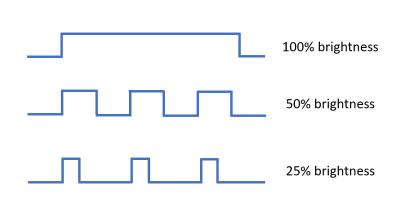
Source: OLED-info
You can see that the light is always on at 100% brightness. The panel switches between on and off at equal intervals when the brightness is reduced to 50%.
However, when the brightness is reduced further, the screen remains off for longer periods of time than it goes on. As a result, there is a significant flicker effect at extremely low brightness levels.
What is DC Dimming?
DC dimming is a method of controlling the brightness of a circuit by altering the power supplied to it. Because Power = Voltage x Current, altering either of these inputs will change the amount of power sent to the display screen, and hence its brightness.
Isn’t it rather straightforward? So, why isn’t DC dimming being used in AMOLED smartphones?
Smartphone makers have been employing DC dimming on LCD screens for years, although it was only later that they began to include it on AMOLED screens.
This is attributable to the fact that DC dimming has a significant disadvantage. Colors on OLED displays are frequently distorted at low brightness levels.
A change in voltage in OLED screens can alter the colors produced. As a result, the perceived quality of the smartphone display may suffer dramatically at lower voltage levels.
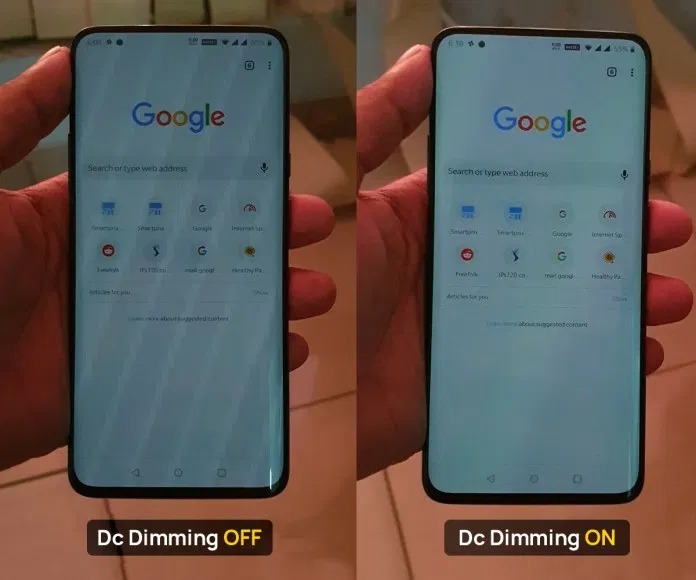
Pictures were taken at lower display brightness | Source:smartprix
What is the solution?
Manufacturers of smartphones are becoming increasingly aware of the potential health risks related to PWM dimming. Nevertheless, given how only a small percentage of the population is affected by PWM flickering and the drawbacks of DC dimming on AMOLED panels, contemporary smartphone makers have opted to provide it as an add-on feature.
OnePlus already has stated that it is experimenting with DC dimming on its phones. It’s possible that the functionality will be implemented in a future update.
Actually, Chinese smartphone manufacturers appear to be enthusiastic about this feature.
Xiaomi, OPPO, Vivo, and even Meizu have verified that DC dimming is available on their current or forthcoming devices.
Regardless of the fact that PWM dimming may cause some users discomfort, the majority of people will not notice a change. It’s crucial to understand that your sensitivity to the flicker effect determines how it affects you.
Don’t blame PWM dimming for your eye strain or headache just yet if you’ve been staring at your smartphone screen for far too long.
Try to develop healthy smartphone habits, such as adjusting your display brightness to a comfortable level (rather than having it at 100% all of the time) and maintaining a reasonable distance between your smartphone screen and you.
How do other manufacturers reduce brightness on AMOLED panels, such as Samsung, Apple, and LG?
To eliminate flicker on their OLED screens for smartphones and TVs, manufacturers such as Samsung, Apple, and LG use PWM in combination with Analog brightness control.
In this method, the initial dimming is accomplished by decreasing the current via OLEDs, and PWM is used for low brightness levels.
Xiaomi is another company that has introduced support for DC dimming to the Xiaomi Mi 9. DC Dimming is also supported on the Black Shark 2, a gaming phone made by Xiaomi’s subsidiary.
PWM effect kicks in at less than 50% brightness on the iPhone X display.
Source: IXBT
In its high-end phones, Oppo has begun to provide DC Dimming a Flicker-free display option.
PWM is still used by Huawei, and screen flicker is highly noticeable on flagships such as the Huawei P30 Pro. The DC Dimming option may be provided via an OTA update, which is a good thing.
PWM isn’t the only factor to consider.
Flicker can also be caused by low refresh rate displays (below 60Hz) or low refresh rate videos. On low refresh rate screens, scrolling or fast animations are another cause.
Avoid using your phone in a dark environment as much as possible to protect your eyes from flickering. You can choose high-refresh-rate displays and monitors (more than 120Hz) at work.
If you have an OLED display phone, you should avoid watching videos at the lowest brightness level. Flicker isn’t visible at 50% brightness on the iPhone X, however, it is visible at lower brightness levels.
However, this isn’t always a viable option. When the brightness is decreased below 100%, the Huawei P30 Pro exhibits extreme flickering.
Smart Phones list that supports DC Dimming
- Xiaomi Mi 9
- Xiaomi Mi 8
- Black Shark 2
- Redmi K20 Pro and Redmi K20
- OnePlus 7 Pro and OnePlus 7(Support will also be extended to previous OnePlus devices. )
- Oppo Reno 10X Zoom
- Realme X
How to Enable DC Dimming (No Root)?
Step 1: Go to Google Play.
Step 2: Search and Install Activity Launcher.
Step 3: Search for the “flick” in the bar and select “Anti-Flicker Mode” from the setting app.
Step 4: Just enable it then, like below.
Step 5:That’s all there is to it.
This test was performed on a One-OS device running the Miui 21.7.21 Beta ROM.
How to enable DC Dimming on Xiaomi Smart Phones?
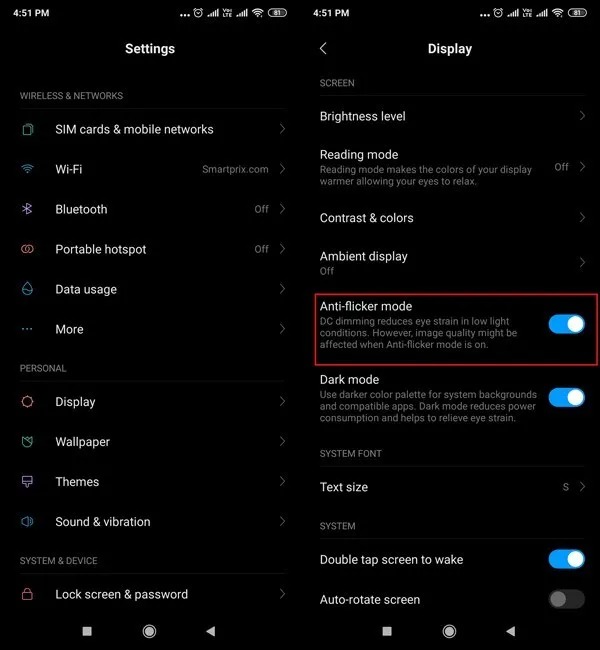
Source:smartprix
Go to display settings on Xiaomi phones running MIUI 10 and enable “Anti-flicker mode.”
How to enable DC Dimming on OnePlus Smart Phones?
Only the 7 Pro and 7 are equipped with this feature at the moment. DC dimming can also be turned on just before nighttime use and turned off afterwards. It would have been easier if there had been an automated scheduler.
Step 1: Go to the main Settings menu and click Utilities from the drop-down menu.
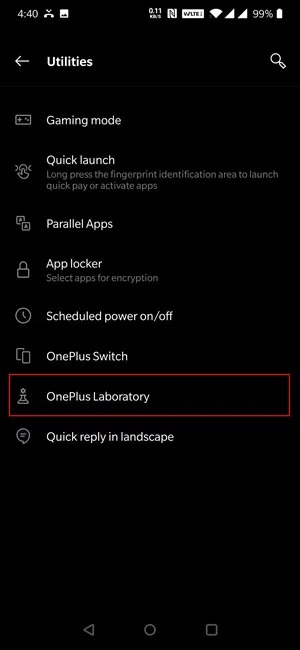
Source:smartprix
Step 2: Next, go to OnePlus Lab and enable DC Dimming.
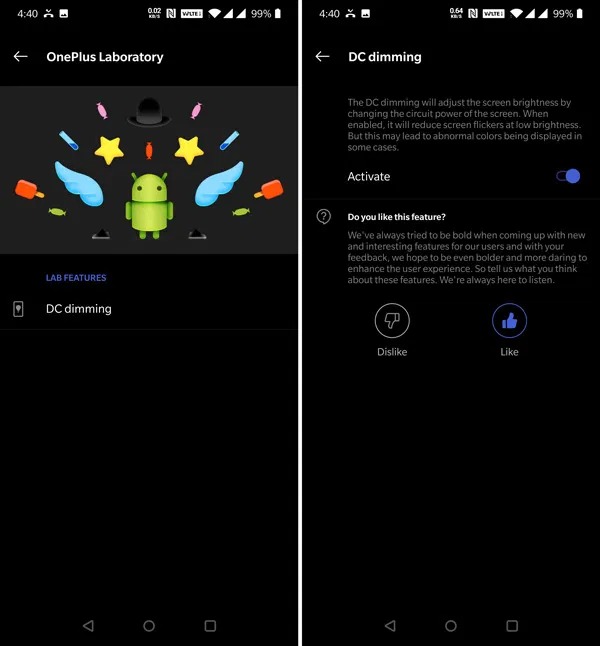
Source:smartprix
How to enable DC Dimming on Oppo and Realme Smart Phones?
Toggle on the “low-light flicker-free eye care” option in Settings>> Display & Brightness on Color OS phones from Oppo and Realme.
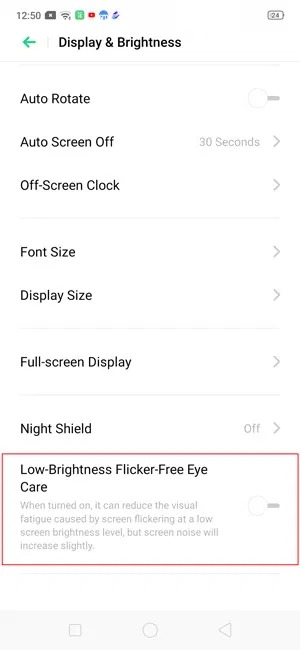
Source:smartprix